If you have more than one port on a box-wall, Z0 and Eeff cannot be determined as there is more than one mode for the transmission line. In this case, your output data will contain "Coupled Port" indicating that there are multiple ports. Even though Z0 and Eeff can not be determined, the S-parameter data is still valid.
However, Sonnet can be used to compute the common and differential mode Z0 and Eeff values for two symmetrical coupled lines. The common and differential mode are very similar to the even mode and odd mode used by popular transmission line couplers (see Interpreting Z0 and Eeff below). To create a project which can be used to find any of these quantities, start with a four-port coupled line circuit like the one shown below:
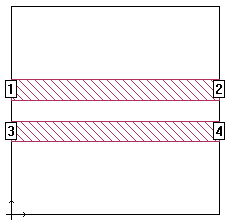
Notice that the lines are placed precisely in the center of the box. This is not necessary in many cases, but we suggest you do this to force the symmetry between the two lines.
Next, renumber your ports as shown below. The left two ports (+1/-1) represent the differential, or odd mode. The right two ports (+2/+2) represent the common, or even mode:
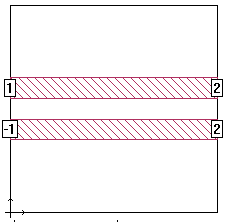
To renumber a port, right-click on the port and select Port Properties. This opens the Port Properties dialog box where you can change the port number.
There is a subtle difference between the even/odd mode and common/differential mode Z01. Sonnet computes the common and differential mode Z0 values, but you can easily calculate the even and odd mode Z0 values by either multiplying or dividing the sonnet results by two as shown in the equations below:
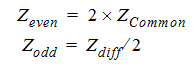
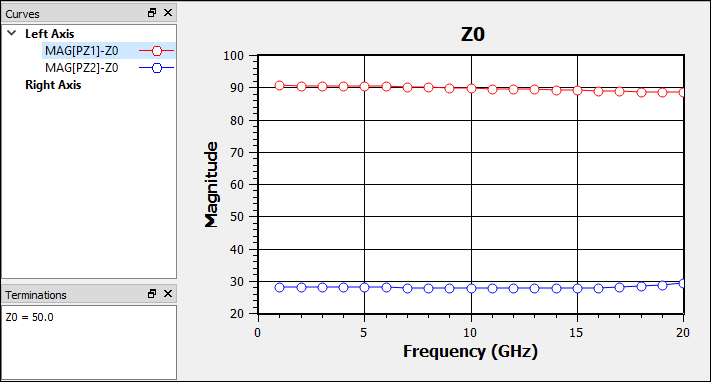
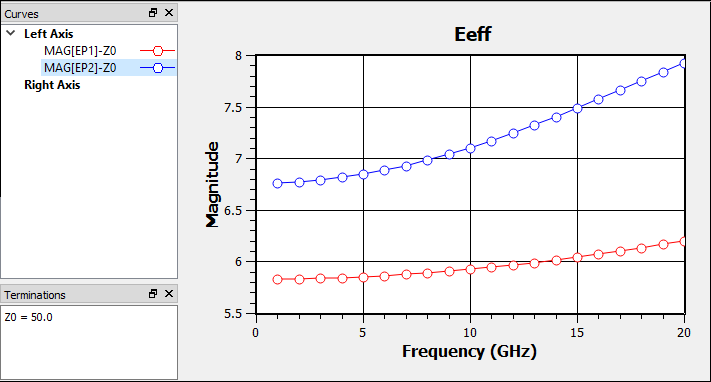
The Eeff values do not need to be modified. Shown below are plots of the differential mode (port 1) and common mode (port 2) Z0 and Eeff. Since the differential mode Z0 is about 90 ohms, the odd mode Z0 is about 45 ohms. And since the common mode Z0 is about 28 ohms, the even mode Z0 is about 56 ohms. As can be seen by the plots, the Z0 and Eeff values are all a function of frequency.
1]"Characterization of differential interconnects from time domain reflectometry measurements" by A. Tolescu and P. Svasta